Oral Health and Its Effects on Heart Health
Oral Health and Its Effects on Heart Health
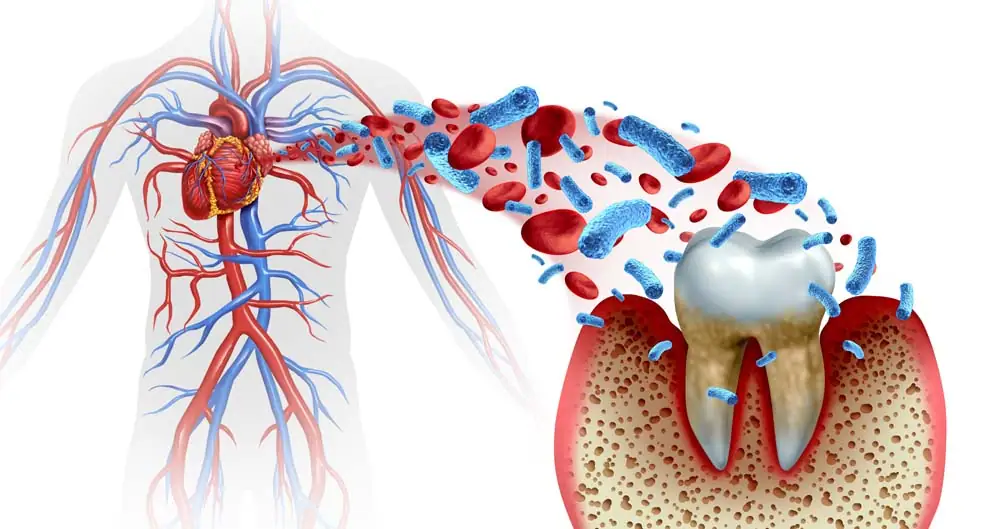
Oral health is often viewed in isolation, with a primary focus on teeth and gums. However, the mouth is a window to overall health and can signal systemic conditions long before they become apparent. Increasingly, research underscores a significant link between oral health and heart health, shedding light on the importance of maintaining a healthy mouth to support a healthy heart.
Understanding Oral Health
Oral health encompasses the well-being of the entire oral cavity, including the teeth, gums, and supporting tissues. Key aspects of oral health include:
- Dental Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups.
- Gum Health: Prevention and management of periodontal (gum) diseases.
- Oral Microbiome: The balance of bacteria within the mouth.
Neglecting oral health can lead to dental cavities, gum disease, and more serious infections. But the implications extend beyond the mouth, potentially influencing cardiovascular health.
The Connection Between Oral Health and Heart Health
The link between oral health and heart health is predominantly centered around periodontal disease. Periodontal disease, or gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth. Here’s how poor oral health can impact the heart:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the mouth can trigger inflammation throughout the body. This systemic inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the hardening and narrowing of the arteries, which is a leading cause of heart attacks and strokes.
- Bacterial Spread: Harmful bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream through gum tissue. Once in the bloodstream, these bacteria can attach to fatty deposits in the coronary arteries (the arteries supplying blood to the heart), contributing to the formation of clots. These clots can obstruct blood flow, leading to heart attacks.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: The endothelium is a thin membrane lining the inside of the heart and blood vessels. Poor oral health can lead to endothelial dysfunction, reducing the vessels’ ability to regulate blood pressure and blood clotting, which are critical factors in heart health.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Studies have shown that individuals with periodontal disease have a higher risk of developing heart disease. The American Heart Association (AHA) acknowledges a significant association between periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease, suggesting that maintaining good oral hygiene can play a role in preventing heart disease.
Key Studies and Findings
Several studies have provided compelling evidence of the oral-heart health connection:
- Study by the American Heart Association: Published in 2012, this study reviewed over 500 scientific papers and concluded that periodontal disease is associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease independently of traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
- The PAVE Study (Periodontitis and Vascular Events): This research highlighted that treating periodontitis can reduce systemic inflammation and improve vascular function, potentially lowering cardiovascular risk.
- Nobel Biocare’s Global Health Survey: This survey found that people with severe gum disease were twice as likely to have a heart attack compared to those with healthy gums.
Preventative Measures for Oral and Heart Health
Maintaining optimal oral health is crucial for reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Here are essential steps for good oral hygiene and overall health:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit the dentist at least twice a year for cleanings and check-ups. Early detection of gum disease can prevent its progression and subsequent systemic effects.
- Effective Oral Hygiene Practices: Brush teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque from areas where a toothbrush can’t reach. Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce oral bacteria.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit sugary foods and beverages that can promote tooth decay.
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Smoking and using other tobacco products can significantly increase the risk of gum disease and subsequently heart disease.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease. Proper management of such conditions can help maintain oral and overall health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, maintaining a healthier mouth.
Conclusion
The intricate link between oral health and heart health highlights the importance of comprehensive healthcare. By prioritizing oral hygiene and regular dental visits, individuals can reduce the risk of periodontal disease and its potential impact on heart health. This integrated approach to health underscores the adage that prevention is better than cure, paving the way for a healthier mouth and a healthier heart.
AUTHOR : DR. FARIA SABA

Email: dr.fariasaba@lumosdentalcare.com
Dr. Faria Saba is a renowned dental surgeon with an experience of more than 18 years in dentistry. She is the co founder and managing director at Lumos Dental Care.She delivers a wide range of treatments . Areas of expertise Cosmetic dentistry, Dental implants, Laser assisted dentistry.
*Dental Implants .
*Laser Dentistry &
*Cosmetic Dentistry

I like this web site it’s a master piece!